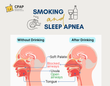
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a prevalent sleep disorder characterized by repeated episodes of partial or complete obstruction of the upper airway during sleep, leading to disrupted breathing patterns. These interruptions can last from a few seconds to minutes and may occur multiple times per hour. Understanding OSA, its symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options is crucial for individuals experiencing sleep-related issues.
Understanding Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
OSA occurs when the muscles at the back of the throat relax excessively during sleep, causing the airway to narrow or close. This obstruction leads to reduced or completely halted airflow, resulting in decreased oxygen levels in the blood. The brain senses this lack of oxygen and briefly awakens the individual to reopen the airway, often without the person being aware of these awakenings.
Symptoms of OSA
Common symptoms of OSA include:
-
Loud Snoring: Often the most noticeable sign, especially reported by a bed partner.
-
Episodes of Breathing Cessation: Witnessed by another person during sleep.
-
Abrupt Awakenings: Accompanied by gasping or choking sensations.
-
Morning Headaches: Due to decreased oxygen levels.
-
Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Falling asleep during activities like reading, watching TV, or even driving.
-
Difficulty Concentrating: Impaired attention and alertness.
-
Irritability or Mood Changes: Due to disrupted sleep patterns.
-
Dry Mouth or Sore Throat Upon Waking: Resulting from breathing through the mouth during sleep.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing OSA:
-
Excess Weight: Fat deposits around the upper airway can obstruct breathing.
-
Neck Circumference: A thicker neck may have a narrower airway.
-
Narrowed Airway: Inherited traits or enlarged tonsils/adenoids can reduce airway size.
-
Being Male: Men are more likely to develop OSA.
-
Age: The risk increases with age.
-
Family History: A genetic predisposition can play a role.
-
Use of Alcohol or Sedatives: These relax the muscles in the throat.
-
Smoking: Increases inflammation and fluid retention in the upper airway.
-
Nasal Congestion: Difficulty breathing through the nose can contribute to OSA.
Diagnosis of OSA
Diagnosing OSA typically involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
-
Medical History and Physical Examination: Assessing symptoms and potential risk factors.
-
Sleep History: Gathering information from the patient and, if possible, from someone who shares the sleeping environment.
-
Sleep Study (Polysomnography): This is the gold standard for diagnosing OSA. It involves an overnight stay at a sleep center where various body functions are monitored during sleep, including brain activity, eye movement, heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and respiratory effort.
-
Home Sleep Apnea Testing (HSAT): For patients with a high likelihood of moderate to severe OSA, a simplified test that can be conducted at home may be recommended.
Treatment Options
Treatment for OSA aims to restore regular breathing during sleep and alleviate symptoms such as loud snoring and daytime sleepiness. Options include:
Lifestyle Modifications
Weight Loss: Even a modest reduction in weight can improve symptoms.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce OSA severity.
Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives: These substances relax the muscles in the throat, worsening OSA.
Sleeping on One's Side: This position can prevent the tongue and soft palate from resting against the back of the throat.
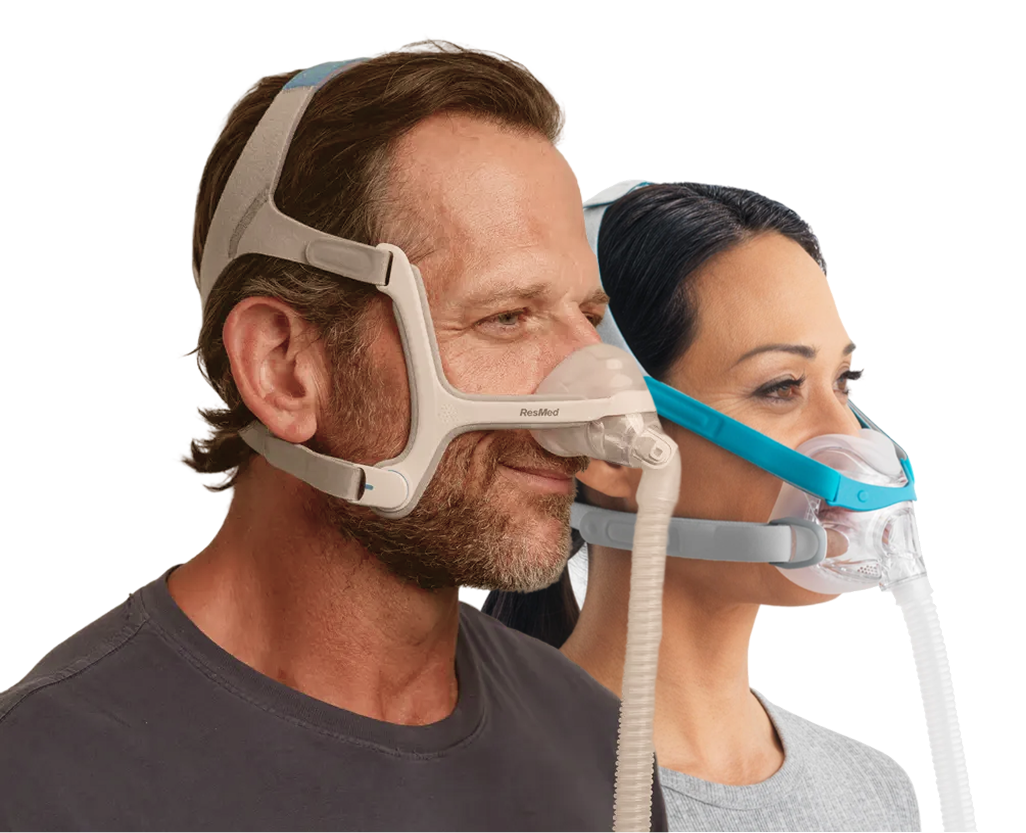
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
How It Works: A machine delivers air pressure through a mask placed over the nose or mouth during sleep. This pressure keeps the upper airway passages open, preventing apnea and snoring.
Benefits: CPAP is highly effective in treating OSA and improving quality of life.
Considerations: Proper mask fit and acclimation to the device are essential for compliance.
Oral Appliances
Function: These devices reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open.
Usage: Particularly useful for individuals with mild to moderate OSA or those who cannot tolerate CPAP.
Fitting: A dentist or orthodontist trained in sleep medicine customizes the device.
Surgical Interventions
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): Removes tissue from the rear of the mouth and top of the throat.
Genioglossus Advancement (GA): Repositions the tongue muscle attachment forward.
Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA): Moves the upper and lower jaw forward to enlarge the airway.
Considerations: Surgery is typically reserved for patients who do not respond to other treatments.
Choosing the Right CPAP Mask
A well-fitted mask is crucial for effective CPAP therapy. There are three main types:
-
Nasal Masks: Cover only the nose and are suitable for those who breathe primarily through their nose.
-
Full-Face Masks: Cover both the nose and mouth, ideal for mouth breathers or those with nasal congestion.
-
Nasal Pillow Masks: Minimal contact design, with small cushions resting inside the nostrils.
Mask Fitting & Adjustments: Many CPAP providers in Melbourne offer mask-fitting services to ensure comfort and a proper seal.
Maintenance & Care of CPAP Equipment
To ensure the longevity of CPAP devices and masks, regular maintenance is essential:
-
Daily Cleaning: Wash the mask, tubing, and humidifier chamber with mild soap and water.
-
Filter Replacement: Change or clean the CPAP machine’s filter as recommended by the manufacturer.
-
Humidifier Care: Use distilled water to prevent mineral buildup.
-
Mask & Cushion Replacement: Over time, the mask and cushions wear out and should be replaced for optimal performance.
Getting a Sleep Study in Melbourne
If you suspect you have sleep apnea but have not been diagnosed, a sleep study (polysomnography) is the best way to confirm the condition.
Types of Sleep Studies Available:
-
In-Lab Sleep Study: Conducted in a sleep clinic, where sleep specialists monitor breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and brain activity overnight.
-
Home Sleep Test (HST): A more convenient and affordable option for individuals with a high probability of moderate to severe OSA.

How to Book a Sleep Study in Melbourne
Several clinics and sleep specialists in Melbourne offer comprehensive sleep studies. Some leading providers include:
-
Melbourne Sleep Disorders Centre – Offers in-lab and home sleep studies with expert diagnosis.
-
Sleep Studies Australia – Provides accessible home sleep testing options.
-
CLM Sleep Co. – Specializes in diagnosing and treating sleep apnea in Melbourne.
The Importance of Treating OSA
Leaving OSA untreated can lead to severe health complications, including:
-
High Blood Pressure & Heart Disease: Repeated drops in oxygen levels strain the cardiovascular system.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: Poor sleep contributes to insulin resistance.
-
Stroke & Cognitive Decline: Increased risk due to reduced oxygen supply to the brain.
-
Depression & Mood Disorders: Sleep deprivation affects mental health.
-
Daytime Fatigue & Accidents: Increased risk of workplace and driving accidents due to lack of focus.
If you experience symptoms of OSA, don’t wait - seek a diagnosis and explore CPAP therapy. Whether you need to buy, rent, or receive expert advice on CPAP machines in Melbourne, reliable providers can help improve your sleep quality. Contact a sleep specialist or CPAP provider today and take the first step towards better sleep and overall health!