Sleep apnea in pregnancy can lead to growth complications or persistent fatigue, which may appear normal but could signal a more serious condition impacting both the mother and the baby. Left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to complications like hypertension, gestational diabetes, and premature deliveries. This blog will discuss causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments for sleep apnea during pregnancy and what reputable providers like CPAP Discount Warehouse can do to ensure safer and more comfortable nights.
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Pregnancy?
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a very common sleep disorder and has been shown to cause significant morbidity in the general population. The development of sleep disorders during pregnancy may be related to anatomical and physiological changes that occur during pregnancy, such as weight gain, uterine enlargement, diaphragmatic elevation, upper airway reorganization, and hormonal changes, such as those associated with estrogen and progesterone. Some survey show that OSA during pregnancy is associated with adverse outcomes for both the mother and the baby, although the exact mechanisms underlying this phenomenon remain unclear.
OSA during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of preeclampsia, gestational hypertension, gestational diabetes (GSD), perinatal depression, and fetal consequences such as growth restriction, congenital anomalies, and neurobehavioral disorders. Various studies have confirmed this association in pregnant women, and further research has identified potential mechanisms underlying this condition, including oxidative stress, autophagy, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction.

Causes of Sleep Apnea During Pregnancy
Sleep apnea during pregnancy, often referred to as sleep apnea pregnancy, typically results from a combination of physical and hormonal changes that affect breathing during sleep.
Weight gain is a key factor. As the body gains fat, especially around the neck and upper airway, the space for airflow becomes more restricted, making it easier for the airway to collapse during sleep.
Hormonal changes also contribute. Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone cause the body to retain fluid, leading to soft tissue swelling in the throat and nasal passages. This can narrow the airway and increase the chances of obstruction.
Nasal congestion is another common issue. Many pregnant women experience stuffy noses due to hormonal effects and increased blood flow, which can make breathing through the nose harder and lead to snoring or disrupted sleep.
Pre-existing conditions that may increase the risk of sleep apnea include:
-
Obesity
-
Hypertension
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
>>> What to Know About Sleep Apnea and Diabetes?
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea in Pregnancy
Recognizing the symptoms of sleep apnea in pregnancy is important for both early intervention and the health of the mother and baby. While many signs may seem like normal pregnancy discomforts, persistent or severe symptoms can point to obstructive sleep apnea, especially in those who are pregnant with sleep apnea.
One of the most common and noticeable symptoms is loud snoring, especially if it’s new or worsens during pregnancy. Snoring may be accompanied by pauses in breathing followed by gasping, choking, or restless movements during sleep. These breathing disruptions often go unnoticed by the individual but may be observed by a sleep partner.
During the day, women experiencing sleep apnea often suffer from:
-
Excessive fatigue or daytime sleepiness, even after what seems like a full night’s sleep
-
Morning headaches, often caused by reduced oxygen levels overnight
-
Difficulty concentrating or mental fog
-
Mood changes such as irritability, depression, or anxiety
-
Frequent nighttime awakenings or bathroom visits
These symptoms result from poor-quality sleep and lack of oxygen during the night. Although fatigue and mood swings are common in pregnancy, the severity and combination of these issues may signal a deeper problem.
When should you be concerned? If you regularly snore loudly, experience gasping or choking during sleep, or feel persistently exhausted during the day, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider. These could be signs of obstructive sleep apnea, a condition that should be addressed early to reduce the risk of complications like high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, and preterm birth.
Early awareness and diagnosis can make a significant difference in managing sleep apnea and promoting a safer, more comfortable pregnancy.

Health Risks for Mom and Baby
Sleep apnea during pregnancy can raise the risk of serious health issues, often categorized under sleep apnea and pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and preterm birth. These conditions not only affect the mother’s health but may also endanger the baby.
Reduced oxygen levels during sleep may impair fetal development, leading to low birth weight or growth issues. For mothers, disrupted sleep increases fatigue, weakens immunity, and contributes to poor concentration.
Mental health is also impacted, with higher chances of stress, anxiety, or prenatal depression. Addressing sleep apnea early helps protect both mother and baby throughout pregnancy.
>>> The Link Between Obesity and Sleep Apnea: Causes & Treatments
How Sleep Apnea is Diagnosed During Pregnancy?
Sleep apnea during pregnancy is commonly diagnosed through a sleep study (polysomnography), which records breathing, heart rate, and oxygen levels during sleep. Depending on the trimester, this test may be done in a lab or at home using a portable device for greater comfort.
Diagnosis can be delayed because many signs, like snoring or tiredness, are often mistaken as normal pregnancy symptoms. This leads to underreporting and missed early detection.
OB-GYNs are key in identifying risks. They may refer patients to a sleep specialist if symptoms such as loud snoring, choking during sleep, or extreme fatigue are present. Collaboration between specialists ensures testing and treatment are safe for both mother and baby.
Early diagnosis allows for timely treatment and reduces complications like preeclampsia or gestational diabetes.
Treatment Options During Pregnancy
Managing sleep apnea during pregnancy depends on the severity of the condition and the stage of pregnancy. A combination of medical support and lifestyle adjustments is often recommended to ensure safety for both mother and baby.
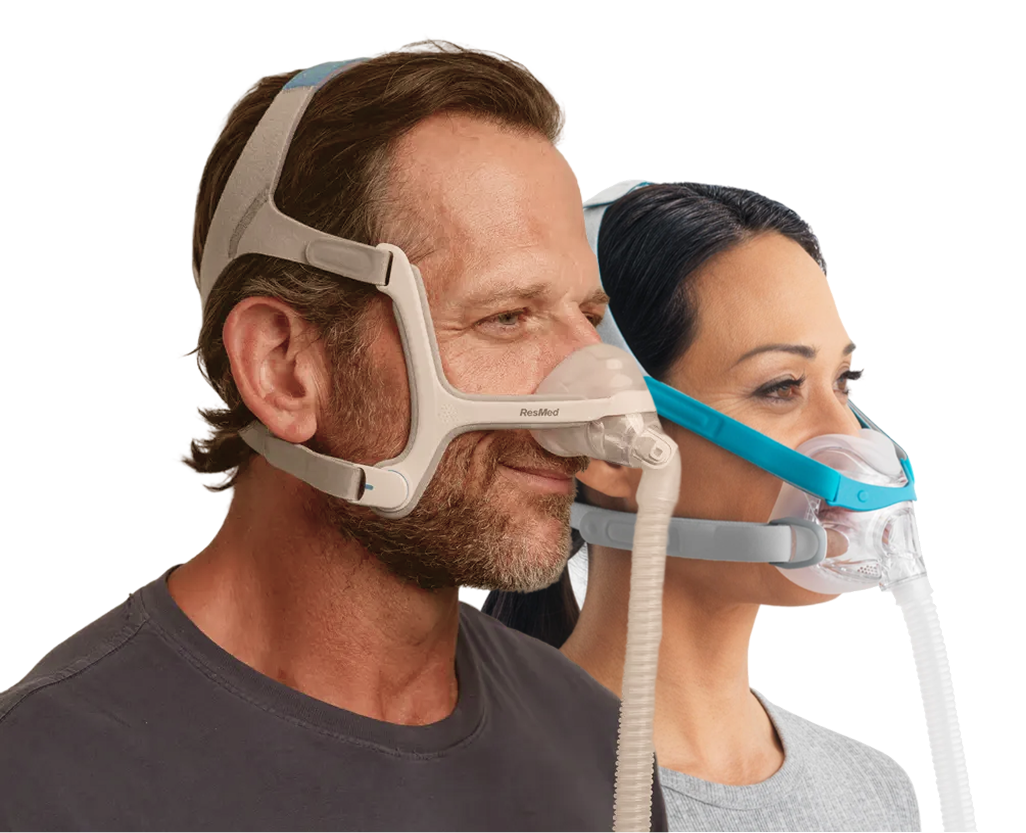
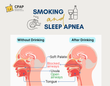
CPAP therapy
For moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea, Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is the most common treatment. It helps keep airways open during sleep by delivering a steady flow of air through a mask. CPAP is considered safe for pregnant women and can improve sleep quality, oxygen levels, and daytime energy.
Lifestyle changes
Simple adjustments can ease symptoms and improve overall health during pregnancy. These may include:
-
Maintaining a healthy weight through doctor-guided diet plans
-
Sleeping on the left side to reduce pressure on airways and improve circulation
-
Avoiding alcohol or sedatives that relax throat muscles
These changes are especially helpful in mild cases or when combined with other treatments.
Nasal congestion
Pregnancy-related hormone shifts often cause nasal swelling and congestion, which can worsen breathing issues at night. To ease this:
-
Use saline nasal sprays or rinses to clear nasal passages
-
Run a humidifier in your bedroom to keep air moist
-
Elevate your head slightly when sleeping to reduce sinus pressure

FAQs
Does pregnancy sleep apnea go away?
For some women, sleep apnea symptoms improve after childbirth, especially if related to pregnancy weight gain or hormone changes. However, if the condition existed before pregnancy or is linked to other risk factors like obesity, it may persist and require ongoing treatment.
Does sleep apnea affect baby during pregnancy?
Yes. Untreated sleep apnea may lead to lower oxygen levels, poor sleep quality, and increased risk of complications like high blood pressure, preeclampsia, or low birth weight. Managing sleep apnea helps support healthy fetal development.
Why do I wake up gasping for air or choking while pregnant?
This could be a sign of obstructive sleep apnea, where the airway becomes temporarily blocked during sleep. Pregnancy-related factors like weight gain, nasal swelling, or soft tissue changes in the throat may contribute. It's important to speak with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea during pregnancy is a serious but manageable condition. Recognizing symptoms like loud snoring, fatigue, or waking up gasping is the first step. Early diagnosis through adapted sleep studies and support from OB-GYNs or sleep specialists helps ensure safe, effective treatment. CPAP therapy, lifestyle changes, and addressing nasal congestion can greatly improve sleep and overall health. Managing sleep apnea not only supports the mother’s well-being but also protects the baby’s development by reducing the risk of sleep apnea and pregnancy complications. With the right care, a healthy pregnancy is absolutely possible. Visit CPAP Discount Warehouse for trusted equipment and guidance to begin your treatment with confidence.
References:
-
Sleep Apnea and Pregnancy: Causes, Signs and Treatment – https://www.brownhealth.org/be-well/sleep-apnea-and-pregnancy-causes-signs-and-treatment – Updated February 6, 2024.
-
Sleep Apnea During Pregnancy – https://www.thebump.com/a/sleep-apnea-during-pregnancy – Updated May 3, 2024.