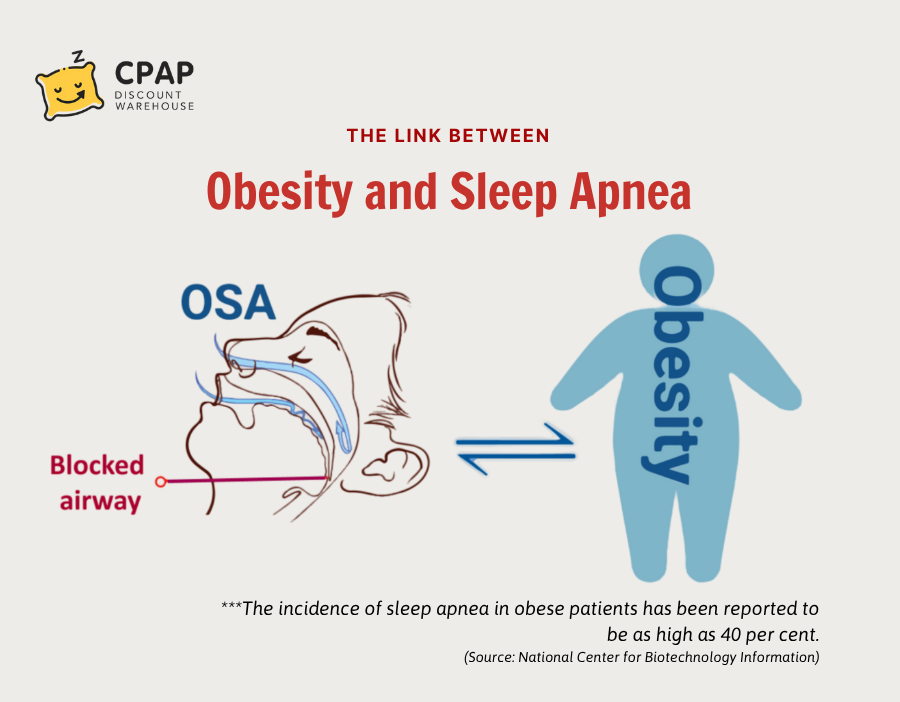
Obesity and Sleep Apnea affect millions of people worldwide as interrelated health problems. An excess of body weight greatly increases the chances of a person developing obstructive sleep apnea, where breathing stoppages occur repeatedly during sleep. This linkage matters very much because untreated sleep apnea drastically reduces quality of life with daytime exhaustion, cardiovascular problems, and metabolic issues plaguing affected individuals. Management and treatment are key, with sites like CPAP Discount Warehouse offering useful data and patient support through the selection of treatment options.
The Relationship Between Sleep Apnea and Obesity
Fatty deposits around the neck and upper airway provide obstruction to the passage of air through the respiratory channel during sleep. This narrowing equates to increased resistance against the upper airway and retrograde flow of air. Hence, overweight individuals tend to develop more of a condition called obstructive sleep apnea - whereby airways are partially or fully collapsed for an intermittent duration, thereby interrupting the very much-needed breathing.
The pathway to cause obstructive sleep apnea is basically multi-factorial, with complexes arising from an interplay between mechanical fat deposition and muscle function in the throat: extra fat around the neck increases pressure on the airway, whereas muscle tone is diminished during sleep leading to increased airway collapse. This translates to frequent pauses in breathing, disruption in sleep architecture, and hypoxemia, casting a disastrous nail on the coffin of their well-being.

Obesity and Sleep Apnea Statistics
Overweight and sleep apnea, along with obesity, are major public health concerns worldwide. The forcing factor for the rising incidence of OSA is overweight and obesity; also, more than 65% of Australians are overweight or obese. Nearly a billion people worldwide are suffering from OSA; many of them are overweight or obese.
The risk of sleep apnea increases significantly with an increase in body weight. Typically, this kind of apnea tends to target men more than women, and the older an individual gets, the more prevalent the disorder becomes. While 40 years may be apparent enough, it grows in strength especially after 40 years. Sleep apnea is much higher in people with a high BMI that is in excess of 30, and the increase is frequently combined with other complications related to obesity.
This growing prevalence places a heavy burden on healthcare systems worldwide. The cost of managing sleep apnea and obesity-related complications, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes, strains medical resources, emphasizing the need for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Health Risks of Sleep Apnea and Excess Weight
Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Health
Sleep apnea, especially when linked with obesity, poses significant risks to cardiovascular health. Breathing is constantly being disrupted, which lowers oxygen levels and in turn triggers high blood pressure and heartache. This connection between obesity sleep apnea and hypertension can result in hypertension, irregular heartbeats, heart attacks, and strokes. Fatness, sleep-related breathing problems, and high blood pressure form a vicious cycle, as each condition worsens if left untreated.
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome and Sleep Apnea
Wherein inadequate breathing during sleep leads to high levels of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream. In many cases, OHS is also accompanied by obstructive sleep apnea, which greatly intensifies these feelings of tiredness during the day as well as shortness of breath. Both of these conditions need an immediate doctor’s visit and special treatment plans to make breathing easier and improve general wellness.

>>> Life Expectancy of Sleep Apnea: What You Need to Know
Childhood Obesity and Sleep Apnea
Childhood obesity is increasingly linked to the development of sleep apnea, posing serious health risks for young individuals. Early warning signs include loud snoring, restless sleep, daytime fatigue, and behavioral issues such as irritability or difficulty concentrating. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial to prevent long-term complications.
Early diagnosis and intervention can dramatically improve outcomes for children with sleep apnea. Addressing excess weight through healthy lifestyle changes, combined with appropriate medical treatment, helps reduce airway obstruction and improve sleep quality. Untreated sleep apnea in children may negatively impact cognitive development and school performance, leading to difficulties with memory, attention, and learning.
Parents and caregivers should be vigilant about these signs and seek professional evaluation to ensure children receive timely care and support.
Sleep Apnea Diagnosis and BMI Chart
Healthcare providers assess the risk of obstructive sleep apnea by combining clinical evaluations with tools like BMI charts and sleep studies. BMI is a key indicator, as higher BMI correlates strongly with increased OSA risk. Sleep studies, including polysomnography, measure breathing interruptions and oxygen levels during sleep to confirm diagnosis.
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor treatment effectiveness and adjust therapies as needed. Continuous monitoring helps manage symptoms, track weight changes, and prevent progression of both Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea, ultimately improving patient health and quality of life.
Obesity Sleep Apnea Treatments
Managing obesity and sleep apnea together requires a comprehensive approach tailored to each individual’s needs. Effective treatment can improve sleep quality, reduce health risks, and enhance overall well-being.
Lifestyle Change
Lifestyle modifications are the foundation of treatment for both obesity and sleep apnea. Dietary adjustments focused on calorie control and balanced nutrition help promote sustainable weight loss. Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health and aids in reducing excess fat, particularly around the neck and abdomen, which can alleviate airway obstruction. Behavioral therapy supports long-term adherence to healthy habits by addressing emotional eating and encouraging positive lifestyle changes.
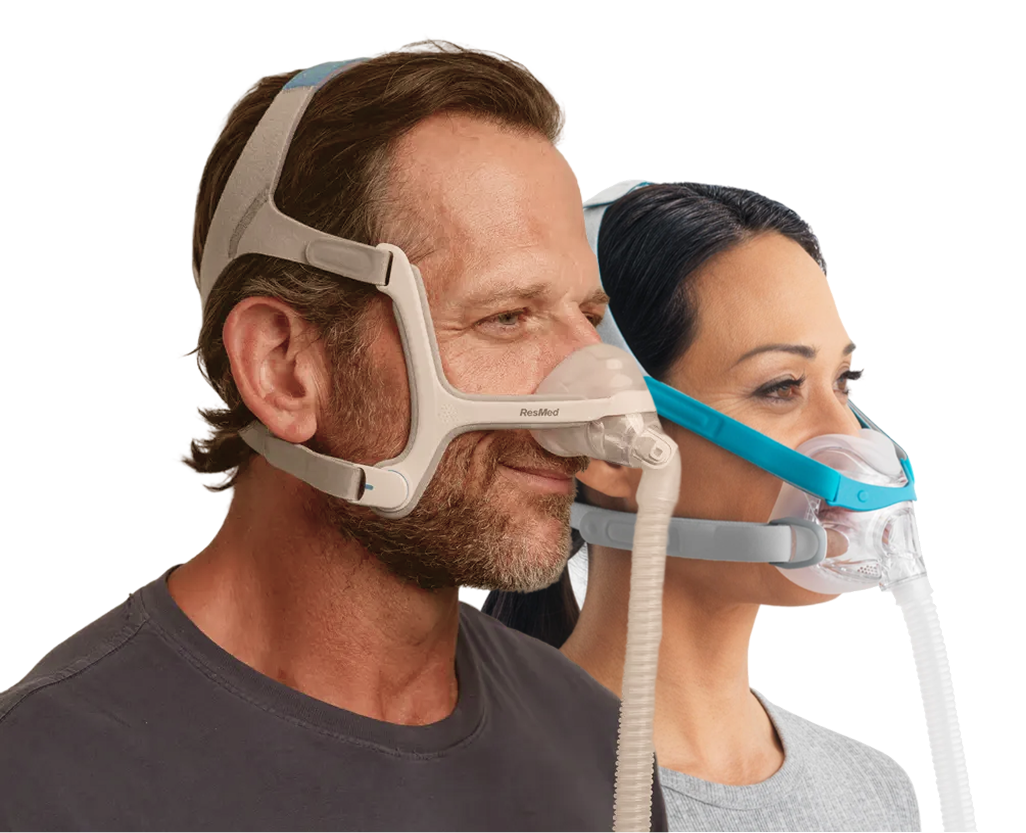
CPAP Therapy
CPAP therapy remains the gold standard for treating obstructive sleep apnea. CPAP machines deliver a steady stream of air through a mask, keeping the airway open during sleep. For many patients, CPAP therapy restores energy levels, reduces daytime fatigue, and facilitates increased physical activity-critical factors in supporting weight loss efforts. Oral devices can be an alternative for mild to moderate cases, repositioning the jaw to maintain airway patency.
Pharmacological & Surgical Treatments
Recent advances have introduced promising pharmacological options such as Tirzepatide, a weight loss drug showing potential in reducing both obesity and sleep apnea severity. Sleep apnea and weight loss drugs like Tirzepatide are gaining attention for their dual benefits in managing these interconnected conditions. Other medications are currently under investigation to target the metabolic and respiratory aspects of sleep apnea and obesity.
For patients with morbid obesity and sleep apnea, bariatric surgery may be recommended when lifestyle changes and medication are insufficient. This surgery not only aids in substantial weight loss but also often leads to significant improvements or resolution of sleep apnea symptoms, greatly improving overall quality of life.

FAQs About Sleep Apnea and Obesity
Is sleep apnea reversible with weight loss?
Yes, weight loss can significantly reduce the severity of obstructive sleep apnea and, in some cases, even reverse it. Reducing excess fat around the neck helps open airways, improving breathing during sleep. However, the extent of reversibility varies depending on individual health factors.
Can sleep apnea be cured?
While there is no universal cure, sleep apnea can be effectively managed with treatments like CPAP therapy, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery. Managing obesity plays a crucial role in controlling symptoms and preventing complications.
How to lose weight with sleep apnea?
Starting CPAP therapy can restore energy and reduce daytime fatigue, making it easier to engage in physical activity. Coupled with a balanced diet and behavioral support, patients can achieve sustainable weight loss that improves both obesity and sleep apnea symptoms.
>>> What to Know About Sleep Apnea and Diabetes
Conclusion
The connection between obesity and sleep apnea is significant and complex. Excess weight contributes to airway obstruction during sleep, increasing the risk of serious health issues. Comprehensive care-including lifestyle modification, CPAP therapy, and medical treatments-is essential to effectively manage both conditions. Consulting a sleep clinic or healthcare provider is the first step toward better health. At CPAP Discount, we offer trusted CPAP devices and expert guidance to support your journey to improved sleep and well-being.