What is Metabolic Syndrome?
-
High blood pressure: blood pressure of 130 mmHg (upper value) and/or 85 mmHg (lower value) and above.
- High blood sugar: fasting blood sugar level equal to or greater than 100 mg/dL. A value between 100 and 125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes. A value above 125 mg/dL likely indicates type 2 diabetes.
- Hypertriglyceridemia: triglyceride level equal to or greater than 150 milligrams per deciliter of blood (mg/dL)
-
Excess belly fat: waist circumference greater than 102 cm in men and 89 cm in women
-
Abnormal cholesterol levels: HDL cholesterol level below 40 mg/dL in men or below 50 mg/dL in women.

>>>> The Link Between Obesity and Sleep Apnea: Causes & Treatments
What are 5 symptoms of metabolic syndrome?
Not all causes of iron deficiency anemia lead to noticeable symptoms. So, your symptoms will depend on how severe your anemia is and what’s causing it. For example, mild iron deficiency may not cause any symptoms at all. More advanced iron deficiency anemia can cause symptoms for some people, such as:
-
Fatigue or weakness.
-
Pale or sallow skin.
-
Shortness of breath during routine activities.
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness.
-
Cold hands and feet.
-
Brittle nails or hair loss.
The conection between metabolic syndrome and sleep apnoea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Metabolic Diseases
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), especially in the context of morbid obesity, is closely linked to a range of metabolic disturbances. One such condition is obesity hypoventilation syndrome, often accompanied by OSAS. Affected individuals typically experience excessive daytime sleepiness and loud snoring, along with clinical signs like cyanosis, rales, right heart strain, and elevated neck circumference. These patients exhibit daytime hypercapnia and hypoxemia and often have coexisting conditions such as hypertension and insulin resistance.
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome may significantly contribute to the development of metabolic syndrome by activating sympathetic pathways, increasing leptin and aldosterone, promoting insulin resistance, and inducing oxidative stress. These shared mechanisms also increase cardiovascular disease risks
Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Metabolic Syndrome
Severe sleep apnea is often associated with metabolic syndrome traits such as high blood pressure, elevated fasting glucose, abdominal obesity, low HDL, and high triglycerides. These patients may also show increased inflammatory markers like TNF-alpha and IL-6, as well as insulin resistance. A positive correlation has been found between sleep apnea severity and markers such as body fat, glucose, leptin, and uric acid.

Sleep Apnea and Metabolic Syndrome treatments
Lifestyle Changes
Healthy lifestyle involves a low-calorie diet and regular physical exercise. It is highly recommended for all obese OSA patients, regardless of severity. Meta-analysis shows that lifestyle changes can significantly reduce blood pressure, fasting glucose, and waist circumference, contributing to a lower risk of MetS.
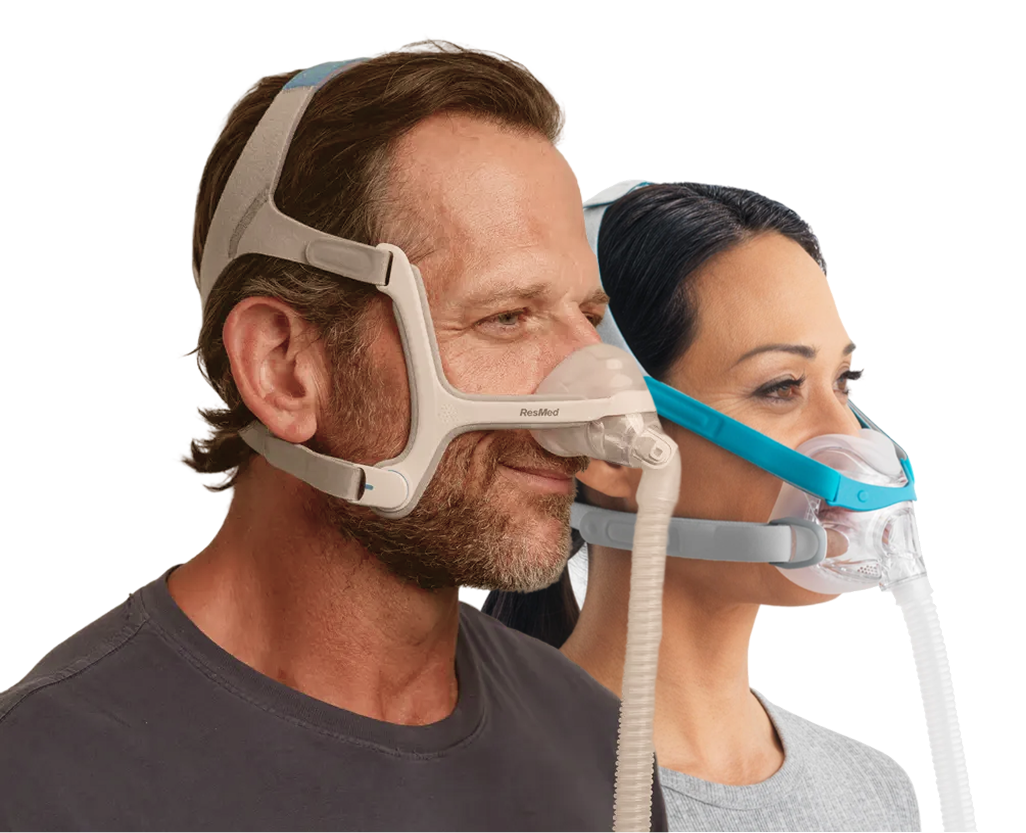
CPAP for the Metabolic Syndrome with OSA
Upper Airway Surgery
Mandibular Advancement Device (MAD)
MAD is a dental device used primarily in patients with mild to moderate OSA. It works by advancing the lower jaw to prevent airway obstruction during sleep.

>>> Learn more right here: The Role of Diet in Sleep Quality
FAQs
How does obesity affect sleep apnea?
Obesity is the most important risk factor for the development of OAS. According to the results of several large-scale epidemiological studies, 58% of moderate and severe OAS cases are related to obesity.
Can sleep apnea cause metabolic syndrome?
Yes, patients with OAS have higher blood pressure, higher fasting insulin levels, greater insulin resistance, lower high-density lipoprotein levels, and a higher incidence of metabolic syndrome.
How to break metabolic syndrome?
Changing your lifestyle to improve your heart health is the first choice for treating metabolic syndrome. You may need to see a nutritionist and a physical therapist to find a diet and exercise program that is right for you. If lifestyle changes do not produce results, you may need medication or weight loss surgery.