Snoring
Snoring
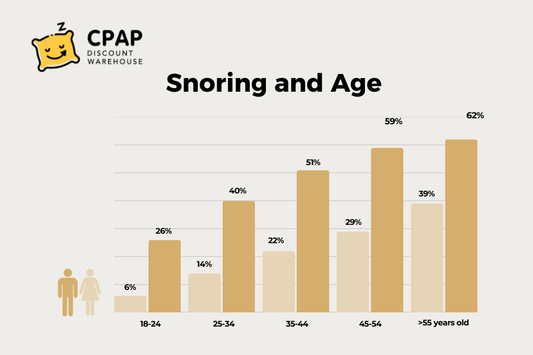

Why does snoring get worse with age?
Snoring can begin at any age, but it shouldn't be considered normal. In fact, it's often a sign that something is blocking your airflow during sleep. This usually happens when...
4 minutes read
What Causes Snoring in Females?
Loud nighttime breathing, often characterized by disruptive and worrisome sounds, is a common issue experienced by many individuals worldwide. While often seen as a source of humor or frustration, snoring...
5 minutes read
How to Stop Snoring?
Loud night breathing is a commonplace issue that impacts hundreds of thousands of humans worldwide. Not most effective can it's bothersome to the individual snoring, however it can also disrupt...
4 minutes read
Snoring is a common issue that occurs when airflow through the nose or mouth is restricted, disrupting sleep. While occasional snoring is typically harmless, chronic snoring can raise the risk of health problems such as stroke and heart disease. Gaining insight into the causes and remedies for snoring is essential for enhancing sleep quality and promoting overall health.
Is snoring normal?
Snoring occurs when throat tissues vibrate noisily due to obstructed airflow during sleep. Occasional snoring is usually harmless. However, snore loudly can signal health issues like sleep apnea. It can also disturb sleep for the person snoring and others nearby.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of snoring?
Snoring is typically identified by a noisy, raspy sound during sleep. Key symptoms include loud, irregular snoring, choking or gasping sounds, and disrupted sleep.
It often stems from blocked or narrowed airways. Due to factors like nasal congestion, obesity, enlarged tonsils, or a deviated septum. Lifestyle habits such as smoking or excessive alcohol use can also contribute.
If snoring is paired with symptoms like excessive daytime fatigue, breathing difficulties during sleep, or pauses in breathing. It could signal a more serious condition such as obstructive sleep apnea. In such cases, seeking medical evaluation is essential to diagnose and treat any underlying health concerns.
When to see a doctor?
You should visit your doctor if:
- Snoring bothers you or your family, you may experience gasping or choking while sleeping.
- If you have a partner, it is recommended that they accompany you to the doctor. They can describe to your doctor what happens while you sleep.
- Snoring indicates that you have sleep apnea, your doctor may refer you to a sleep specialist. They may also recommend conducting an overnight sleep study.


Snoring is more common than many people realize.
Nearly 24% of men frequently snore loudly, and surprisingly, about 17% of women also experience snoring.
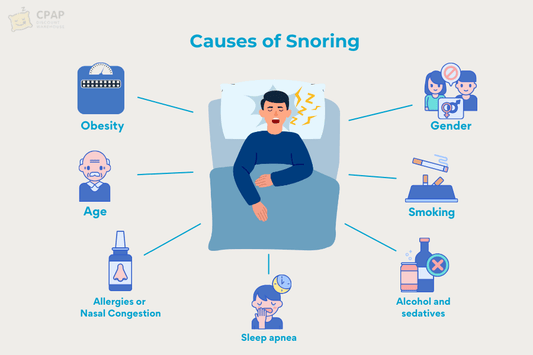
What Causes Snoring?
Snoring mainly occurs when blockages or narrowing affect the airways. This can be due to nasal congestion, obesity, large tonsils, or a deviated septum.
Several factors can increase the likelihood of snoring and contribute to sleep apnea:
- Excess weight, particularly around the neck. It can compress the airways and lead to snoring or breathing issues during sleep.
- Aging weakens throat muscles, making the airway more prone to collapse during sleep.
- Men are more likely to snore than women due to differences in airway structure. Though women and babies can also be affected.
- Blocked nasal passages force more airflow through the mouth, increasing the risk of snoring.
- Alcohol relaxes throat muscles, which can exacerbate snoring.
- Smoking inflames and irritates airway tissues, increasing the chances of snoring.
- Sleeping on the back allows the tongue and soft tissues to fall backward, partially blocking the airway.
Complications
Frequent or severe snoring can result in several complications, including:
- Disrupted Sleep
- Relationship Strain
- Daytime Drowsiness
- Increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes.
- They are connected to a higher risk of heart disease. They can also raise the risk of stroke and metabolic disorders.
- Addressing snoring and its root causes is essential for preventing these complications and improving overall health and well-being.
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing the causes and impact of snoring involves several steps to identify potential complications. The typical diagnostic process includes:
- Medical History: Your doctor will look at your snoring patterns and symptoms like tiredness during the day. They will also check for related issues, such as high blood pressure or heart problems.
- Physical Examination: A doctor may check the throat, nose, and mouth. This helps find problems like nasal congestion or swollen tonsils.
- Sleep Diary: Tracking sleep patterns, snoring frequency, and associated symptoms over a week or more. It can provide useful insights into the problem.
- Questionnaires: Epworth Sleepiness Scale, STOP-BANG Questionnair, Polysomnography (Sleep Study) include In-Lab Study and Home Sleep Study
These diagnostic tools help pinpoint the cause of snoring and assess. Whether it leads to complications, guiding effective treatment strategies.
Our products & services:
Animated Dreams of Restful Nights - Exploring Digital CBT-I
What is a Sleep study? 5 Steps to Get Tested for Sleep Apnoea
Sleep Apnea Home Study: When, Why, How, and Troubleshooting Tips
CPAP Machine Care: Essential Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
What Are The Different Types Of CPAP Masks Available?
Living with Snoring
Snoring affects both the individual and their sleep partners, often leading to disrupted sleep, daytime fatigue, and relationship challenges. Recognizing its effects is essential for finding effective solutions.
1. Managing Snoring
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Lose weight, avoid alcohol before bed, and sleep on your side to reduce snoring. Establish a consistent sleep routine and stay well-hydrated.
- Home Remedies: Use nasal strips, humidifiers, or saline sprays to ease nasal congestion and improve airflow.
- Oral Appliances: Devices like Mandibular Advancement Splints (MAS) move the jaw to keep airways open. They help with snoring problems caused by structure.
2. Addressing Underlying Conditions
Persistent or severe snoring may indicate conditions like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). A medical evaluation can identify and treat these issues with options such as:
- CPAP Therapy: Positive airway pressure CPAP to maintain an open airway.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adjustments to address contributing factors.
- Surgical Interventions: Procedures to correct structural problems.
3. Improving Sleep Quality
Better sleep practices can reduce snoring’s effects, including:
- Creating a comfortable sleep environment.
- Avoiding caffeine in the evening.
- Following a regular sleep schedule.
4. Communication and Support
Discussing the impact of snoring with a partner is key. Collaborating on solutions, whether lifestyle changes or medical treatments, fosters mutual understanding and support. Consulting healthcare professionals can also provide guidance.
By making lifestyle changes, using medical treatments, and applying supportive strategies, people can manage snoring. This can improve their quality of life and lessen its effects on themselves and others.
Explore Our Top CPAP Products
-
CPAP Machines
Discover our comprehensive lineup of CPAP machines designed to treat sleep apnea effectively.
Shop now
-
CPAP Masks
Select from a variety of options including full face masks, nasal masks, and nasal pillow masks.
Shop now
-
CPAP Accessories
Find all the essential accessories to optimize your CPAP therapy experience.
Shop now
FAQs
How to stop snoring?
To prevent or quiet snoring, try these tips:
- If you're overweight, lose weight
- Sleep on your side
- Raise the head of your bed
- Nasal strips or an external nasal dilator
- Treat nasal congestion or obstruction
- Limit or avoid alcohol and sedatives
- Quit smoking
- Get enough sleep
What is difference between Snoring and sleep apnea?
Not all snorers suffer from sleep apnea, but the two conditions often go hand in hand. The louder the snoring, the higher the risk of developing sleep apnea. If you suffer from apnea, your sleep partner may notice that your snoring is interrupted by pauses in your breathing. These are episodes of apnea that can occur hundreds of times a night.
Is snoring a warning sign?
Snoring is a common and generally harmless phenomenon. But if your snoring is chronic and noisy, disrupting your sleep, it may be a sign of a more serious problem. Other symptoms such as daytime fatigue, irritability, headaches or lack of air during sleep may indicate sleep apnea.
When should I get help for snoring?
Your snoring has a significant impact on your life or that of your partner. If you feel sleepy during the day, if your breathing stops repeatedly while you sleep, or if you make choking or breathing noises while you sleep, you may be suffering from sleep apnea, which can be serious if left untreated.




